Blood supply of brain ppt delves into the intricate network that sustains the brain’s vital functions, providing a comprehensive understanding of the arterial supply, cerebral circulation, venous drainage, and clinical significance. This presentation unveils the remarkable mechanisms that ensure the brain’s uninterrupted operation, shedding light on the consequences of cerebrovascular accidents and the crucial role of understanding brain blood supply in neurosurgery and neurology.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the major arteries that nourish the brain, examining their intricate pathways and the delicate balance of cerebral blood flow regulation. We will also uncover the significance of the blood-brain barrier in maintaining brain homeostasis, ensuring the optimal environment for neural activity.
Blood Supply of the Brain: Blood Supply Of Brain Ppt
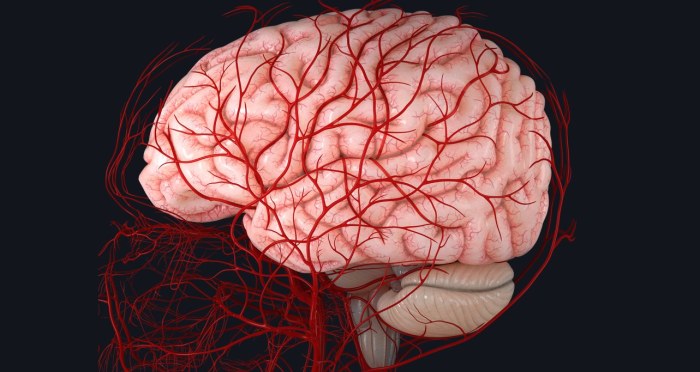
The brain requires a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to function properly. This supply is provided by a complex network of arteries and veins that work together to deliver blood to the brain and remove waste products.
Major Arteries that Supply Blood to the Brain
The major arteries that supply blood to the brain are:
- The internal carotid arteries (ICAs) supply blood to the front and sides of the brain.
- The vertebral arteries (VAs) supply blood to the back of the brain.
The ICAs and VAs join together to form the circle of Willis, a ring of arteries that surrounds the base of the brain. The circle of Willis ensures that the brain continues to receive blood even if one of the major arteries becomes blocked.
Blood supply to the brain is a crucial topic, especially for those concerned about neurological disorders. Interestingly, even animated characters like Nemo from nemo might appear in one could be affected by these conditions. However, understanding the blood supply to the brain remains essential for comprehending its function and addressing potential issues.

Cerebral Circulation
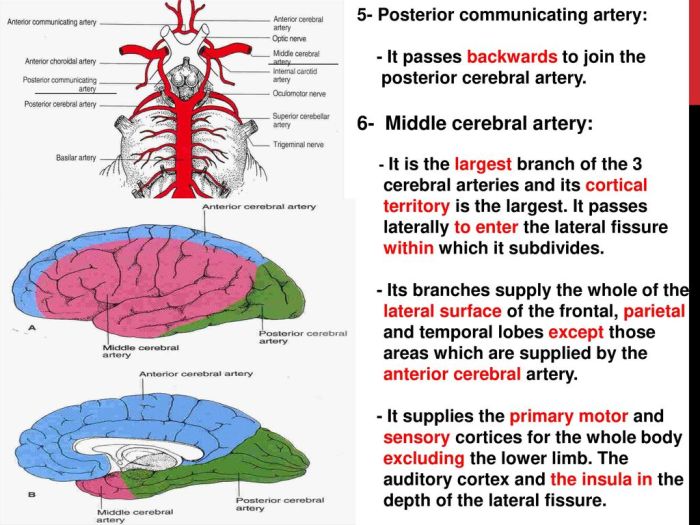
Cerebral circulation refers to the flow of blood to the brain, ensuring a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients. Understanding this circulation is crucial for maintaining brain health and preventing neurological disorders.
- Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow:The brain has intrinsic mechanisms to regulate blood flow in response to its metabolic demands. This regulation involves the dilation or constriction of cerebral blood vessels, controlled by factors such as arterial carbon dioxide levels and neural activity.
- Role of the Blood-Brain Barrier:The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a semipermeable membrane that separates the brain’s extracellular fluid from the blood. It acts as a protective barrier, preventing the entry of harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass through. The BBB plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the brain, protecting it from potential toxins and pathogens.
Venous Drainage of the Brain
The venous drainage of the brain is a complex system that ensures the return of blood from the brain to the heart. It involves a network of veins and sinuses that collect blood from the brain tissue and drain it into the jugular veins.The
cerebral venous system is divided into two main components: the superficial system and the deep system. The superficial system consists of the dural sinuses, which are large channels that run along the inside of the skull. The deep system consists of the cerebral veins, which are smaller channels that run within the brain tissue.The
dural sinuses are formed by the dura mater, which is the tough outer layer of the meninges (the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord). The sinuses are lined with endothelial cells and contain valves that prevent backflow of blood.
The sinuses drain into the jugular veins, which carry blood back to the heart.The cerebral veins are smaller than the dural sinuses and run within the brain tissue. They collect blood from the brain tissue and drain it into the dural sinuses.
The cerebral veins are also lined with endothelial cells and contain valves that prevent backflow of blood.The venous drainage of the brain is an essential part of the brain’s circulation. It ensures that the brain receives a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients and that waste products are removed from the brain.
Clinical Significance
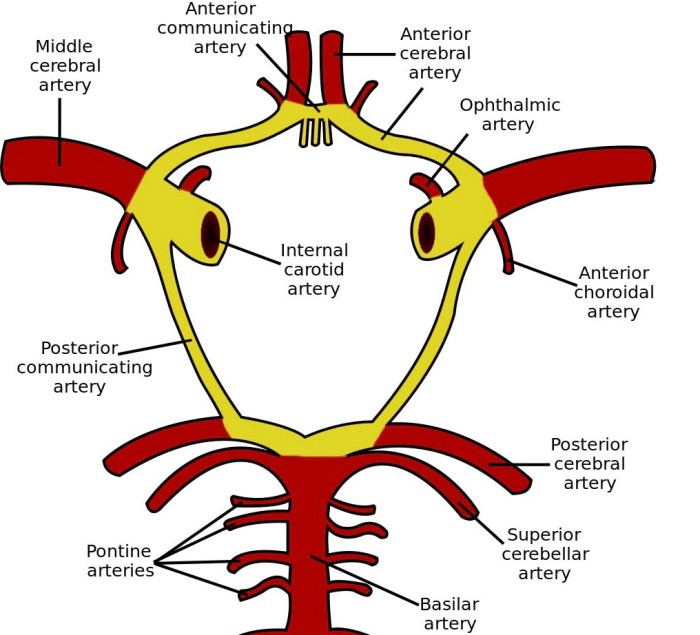
Understanding the blood supply of the brain is crucial for neurosurgery and neurology. It guides surgical interventions, enables the diagnosis of neurological disorders, and helps predict the consequences of cerebrovascular accidents (strokes).
Strokes occur when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, causing damage to brain tissue. The severity of the stroke depends on the location and extent of the blockage. Strokes can lead to a wide range of neurological deficits, including paralysis, speech problems, and cognitive impairment.
Consequences of Cerebrovascular Accidents, Blood supply of brain ppt
- Paralysis: Strokes can damage motor pathways in the brain, leading to paralysis on one side of the body.
- Speech problems: Strokes can affect language centers in the brain, causing aphasia, which impairs speech production and comprehension.
- Cognitive impairment: Strokes can damage areas of the brain responsible for memory, attention, and executive function, leading to cognitive deficits.
- Death: In severe cases, strokes can cause extensive brain damage and lead to death.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the major arteries that supply blood to the brain?
The major arteries that supply blood to the brain are the internal carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries.
What is the role of the blood-brain barrier?
The blood-brain barrier is a semipermeable membrane that surrounds the brain’s blood vessels. It helps to maintain the brain’s homeostasis by regulating the entry of substances into the brain.
What are the consequences of cerebrovascular accidents (strokes)?
Cerebrovascular accidents (strokes) can cause a range of symptoms, including paralysis, speech problems, and cognitive impairment. The severity of the symptoms depends on the location and size of the stroke.