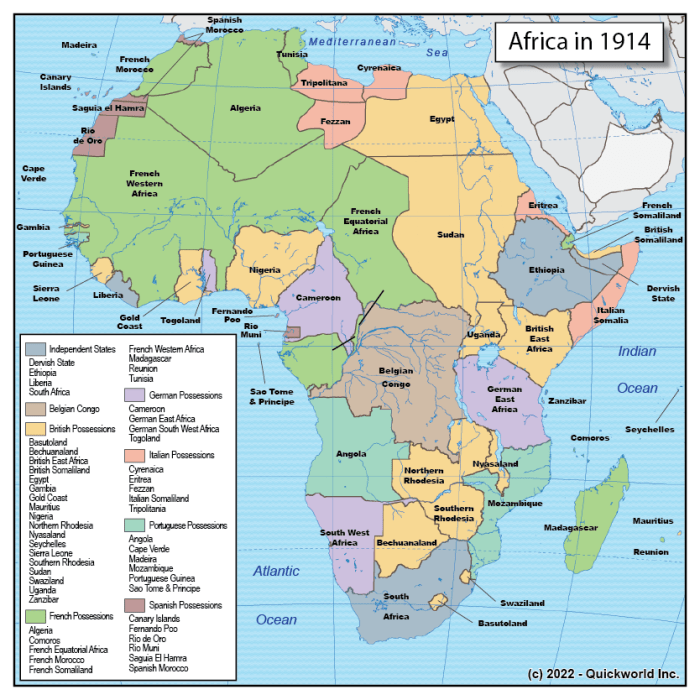
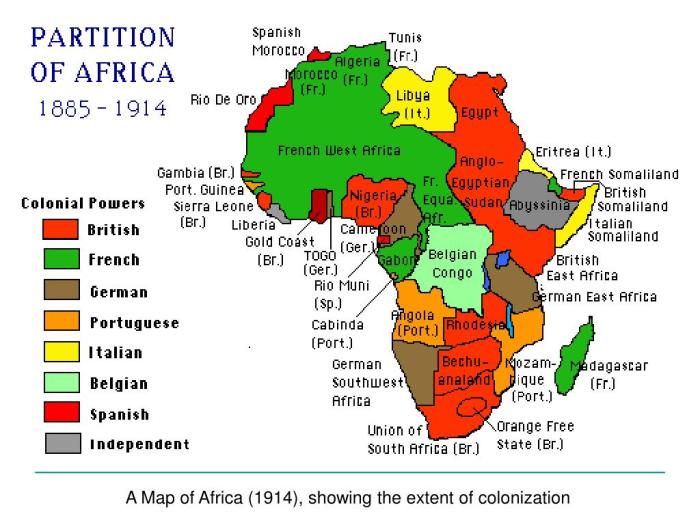
Africa in 1914 map worksheet answers provide a crucial gateway to understanding the continent’s complex political, social, and economic landscape during a pivotal era. This comprehensive resource unveils the intricate web of European colonialism, African resistance, and the profound impact of World War I on the region.
Delving into the intricacies of the 1914 map of Africa, we uncover the geopolitical boundaries that shaped the continent’s destiny. Major cities, territories, and waterways emerge as key players in the unfolding narrative of Africa’s history.
Africa in 1914 Map: Africa In 1914 Map Worksheet Answers
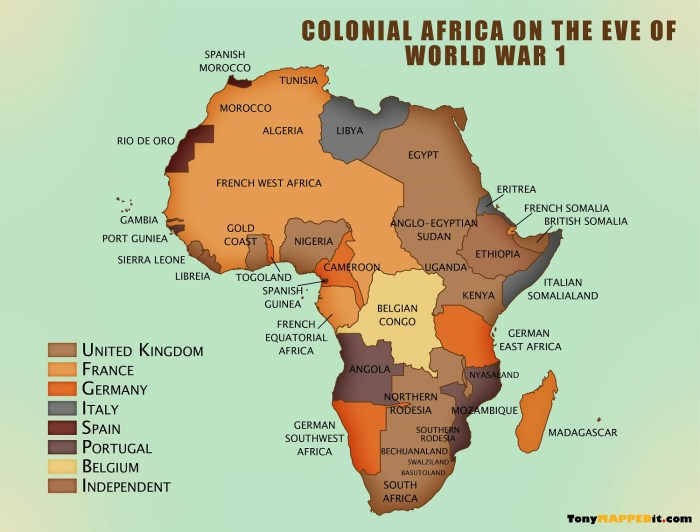
Africa in 1914 was a continent divided, with European powers controlling vast swathes of territory. This map provides a detailed overview of the political and geographical boundaries of Africa at that time, highlighting major cities, territories, and waterways.
The map illustrates the extent of European colonialism in Africa, with European powers such as Britain, France, Germany, Portugal, and Spain controlling large portions of the continent. It also shows the areas of resistance to European rule, such as the Boer Republics in South Africa and the Ethiopian Empire.
European Colonialism in Africa
By 1914, European powers had colonized vast areas of Africa, driven by motives of economic exploitation, political power, and national prestige. The major European powers with colonies in Africa included Britain, France, Germany, Portugal, and Spain.
European colonialism had a profound impact on African societies, leading to the displacement of indigenous populations, the introduction of new crops and technologies, and the exploitation of natural resources. It also led to the establishment of new political and economic structures, which would shape the future development of Africa.
African Resistance to Colonialism, Africa in 1914 map worksheet answers
Despite the overwhelming power of European colonial powers, African resistance to colonialism emerged in various forms throughout the continent. Resistance movements took different forms, from armed uprisings to non-violent protests.
Some notable examples of African resistance movements include the Maji Maji Rebellion in German East Africa, the Herero and Namaqua Rebellion in German South West Africa, and the Ethiopian resistance to Italian invasion.
Economic and Social Conditions in Africa
In 1914, Africa was a continent of diverse economic and social conditions. While some areas had developed thriving economies based on agriculture and trade, others remained subsistence economies with limited access to modern technology.
The impact of colonialism on African economies and societies was complex. While some areas benefited from increased trade and investment, others experienced economic exploitation and social disruption.
World War I and Africa
World War I had a significant impact on Africa. African troops were recruited to fight in the war, and the continent became a battleground for European powers. The war also led to political and economic changes in Africa, as European powers sought to secure their colonies and resources.
Post-World War I Africa
After World War I, Africa underwent significant political and territorial changes. The war had weakened European powers, and African nationalist movements began to emerge. The post-war period also saw the rise of new international organizations, such as the League of Nations, which aimed to promote peace and cooperation.
However, the challenges facing Africa in the post-war period were significant. Colonialism had left a legacy of economic and social inequality, and the continent faced a long and difficult struggle for independence and development.
FAQ Overview
What were the major European powers with colonies in Africa in 1914?
Great Britain, France, Germany, Belgium, Portugal, Spain, and Italy.
How did World War I impact Africa?
It led to the mobilization of African troops, territorial changes, and the weakening of European colonial powers.
What were the consequences of colonialism on African societies?
Political, economic, and social disruption, including the imposition of foreign rule, economic exploitation, and cultural suppression.