Embark on an enlightening journey with the icivics Branches of Power Answer Key, a meticulously crafted guide that illuminates the intricate tapestry of the United States government. Delve into the core principles of the three branches of power, their interdependencies, and the delicate balance they maintain.
This comprehensive resource unravels the complexities of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, empowering you with a profound understanding of their roles, responsibilities, and the checks and balances that ensure a harmonious distribution of power.
Branches of Power Overview
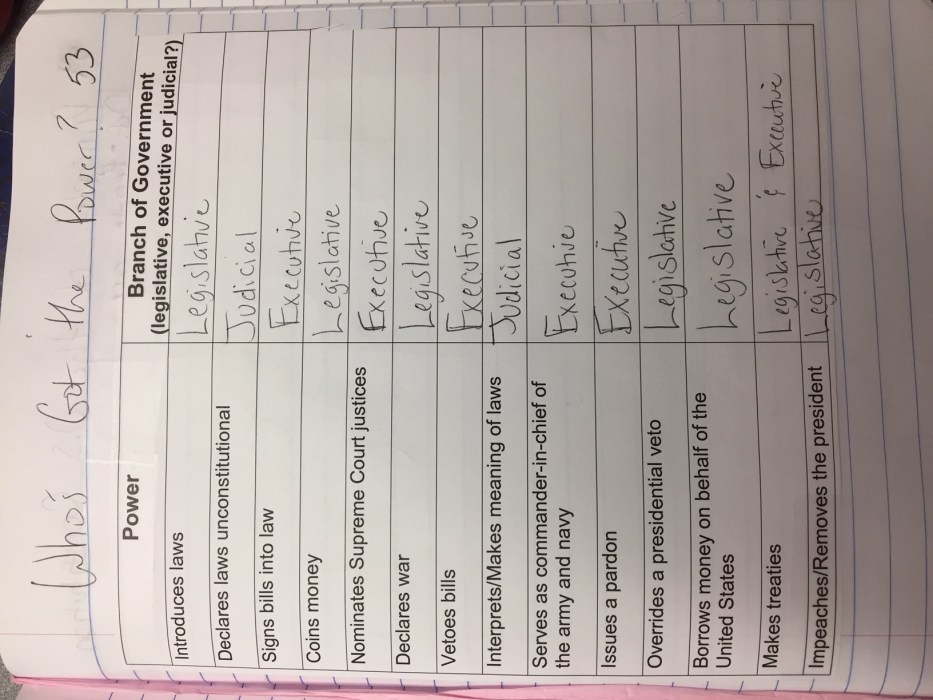
The United States government is divided into three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. Each branch has specific powers and responsibilities, and they interact with each other to ensure that no one branch becomes too powerful.
The legislative branch, consisting of Congress, is responsible for making laws. The executive branch, headed by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws. The judicial branch, consisting of the Supreme Court and lower federal courts, is responsible for interpreting laws and ensuring that they are constitutional.
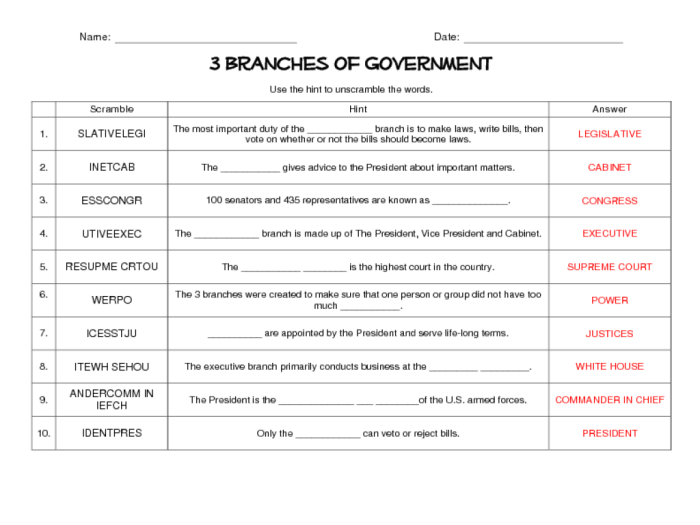
Legislative Branch, Icivics branches of power answer key
Congress is the legislative branch of the federal government. It is made up of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives has 435 members, who are elected to two-year terms. The Senate has 100 members, who are elected to six-year terms.
The legislative process begins when a bill is introduced in either the House of Representatives or the Senate. If the bill is passed by both chambers, it is sent to the President for his signature. If the President signs the bill, it becomes law.
If the President vetoes the bill, it can be overridden by a two-thirds vote of both chambers of Congress.
Executive Branch
The executive branch of the federal government is headed by the President. The President is elected to a four-year term and is responsible for enforcing laws, appointing judges, and conducting foreign policy.
The executive branch is made up of several departments, including the Department of State, the Department of Defense, and the Department of Justice. These departments are responsible for carrying out the President’s policies.
The President also has the power to issue executive orders, which have the force of law. Executive orders are often used to implement the President’s policies or to respond to emergencies.
Judicial Branch
The judicial branch of the federal government is headed by the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court has nine justices, who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The justices serve for life.
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. It has the power to interpret laws and to declare them unconstitutional. The Supreme Court’s decisions are binding on all lower courts.
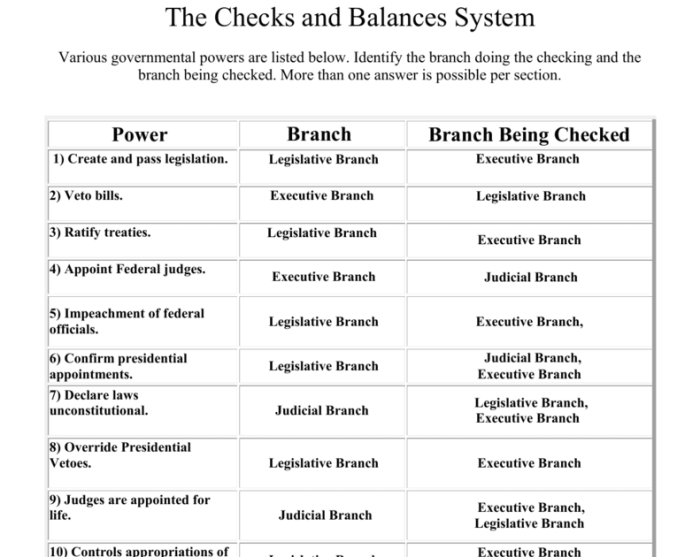
Checks and Balances
The system of checks and balances is a way of ensuring that no one branch of government becomes too powerful. Each branch has the ability to check the powers of the other branches.
For example, Congress can pass laws that limit the President’s power. The President can veto laws passed by Congress. The Supreme Court can declare laws passed by Congress to be unconstitutional.
The system of checks and balances is essential to maintaining a balance of power in the United States government.
User Queries: Icivics Branches Of Power Answer Key
What is the purpose of the icivics Branches of Power Answer Key?
The icivics Branches of Power Answer Key provides a comprehensive understanding of the three branches of government in the United States, their roles, responsibilities, and the system of checks and balances that ensures a balance of power.
How does the legislative branch make laws?
The legislative branch, comprising the House of Representatives and the Senate, creates laws through a complex process involving the introduction of bills, committee review, debates, votes, and ultimately, the President’s signature or veto.
What is the role of the President in the executive branch?
The President serves as the head of the executive branch, responsible for enforcing laws, managing the federal bureaucracy, conducting foreign policy, and appointing key officials, including Supreme Court justices.
How does the judicial branch interpret laws?
The judicial branch, led by the Supreme Court, interprets laws and determines their constitutionality. It has the power of judicial review, allowing it to overturn laws and executive actions deemed unconstitutional.