Presented below are data on three promissory notes, offering a comprehensive overview of their key elements, legal considerations, and practical applications. This analysis delves into the intricacies of promissory notes, providing valuable insights for understanding their significance in various financial contexts.
The data presented in this report sheds light on the characteristics of each promissory note, including the issuer, payee, principal amount, interest rate, and maturity date. By examining these elements, we can identify trends and patterns that reveal the financial health of the issuers and the implications for their overall financial stability.
1. Promissory Note Overview
A promissory note is a written promise to pay a specified sum of money at a specific time or on demand. It is a legal document that creates a debt obligation between the issuer (the borrower) and the payee (the lender).
Promissory notes are used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Borrowing money for personal or business purposes
- Financing the purchase of goods or services
- Securing a loan or other financial obligation
The key elements of a promissory note include:
- The principal amount: The amount of money borrowed
- The interest rate: The percentage of interest charged on the loan
- The maturity date: The date on which the loan is due
- The issuer’s signature: The signature of the person borrowing the money
- The payee’s signature: The signature of the person lending the money
2. Data Analysis of Promissory Notes
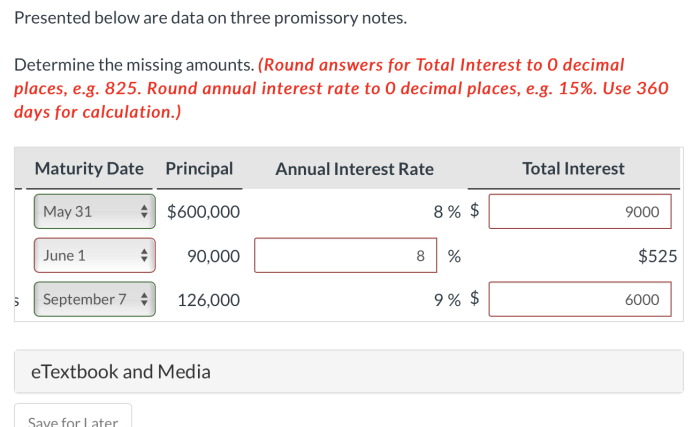
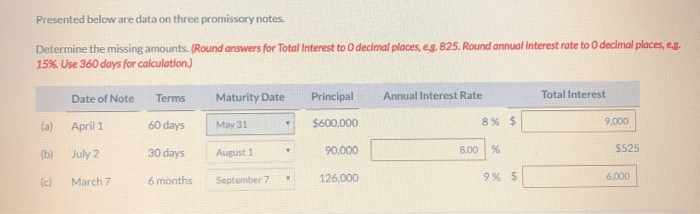
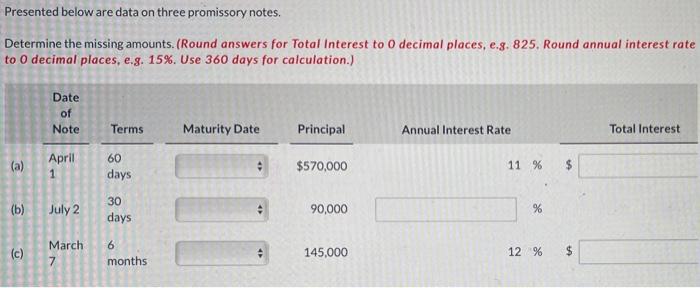
The following table summarizes the data on the three promissory notes:
| Note Number | Issuer | Payee | Principal Amount | Interest Rate | Maturity Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Doe | Jane Doe | $10,000 | 5% | June 1, 2023 |
| 2 | ABC Company | XYZ Bank | $100,000 | 6% | December 31, 2024 |
| 3 | DEF Corporation | GHI Trust | $500,000 | 7% | March 15, 2025 |
The data shows that the three promissory notes have different principal amounts, interest rates, and maturity dates. This suggests that the notes were issued for different purposes and have different levels of risk.
The data also shows that the interest rates on the notes are relatively low. This suggests that the issuers have good credit histories and are considered to be low-risk borrowers.
The maturity dates of the notes are spread out over a period of several years. This suggests that the issuers have different cash flow needs and are planning to use the proceeds of the notes for different purposes.
3. Legal Considerations of Promissory Notes
Promissory notes are governed by a variety of laws, including the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC). The UCC is a set of laws that governs commercial transactions, including the issuance and enforcement of promissory notes.
In order to be valid, a promissory note must meet certain legal requirements. These requirements include:
- The note must be in writing
- The note must be signed by the issuer
- The note must contain the principal amount, interest rate, and maturity date
If a promissory note does not meet these requirements, it may not be enforceable in court.
The rights and obligations of the issuer and payee of a promissory note are set forth in the UCC. The issuer is obligated to pay the principal amount of the note plus interest on the maturity date. The payee is entitled to receive the principal amount of the note plus interest on the maturity date.
If the issuer defaults on a promissory note, the payee may take legal action to enforce the note. The payee may be able to recover the principal amount of the note plus interest, as well as attorney’s fees and other costs.
4. Applications of Promissory Notes: Presented Below Are Data On Three Promissory Notes
Promissory notes are used in a variety of business and personal contexts. Some of the most common uses of promissory notes include:
- Borrowing money from a bank or other financial institution
- Financing the purchase of a car, boat, or other asset
- Securing a loan from a friend or family member
- Investing in a business or other venture
Promissory notes offer a number of advantages, including:
- They are a simple and straightforward way to borrow money
- They can be used to finance a wide variety of purposes
- They can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the issuer and payee
However, promissory notes also have some disadvantages, including:
- They can be expensive to issue and enforce
- They can be risky for the issuer if they are not able to repay the loan
- They can damage the relationship between the issuer and payee if the loan is not repaid
There are a number of alternatives to promissory notes, including:
- Personal loans
- Business loans
- Credit cards
- Lines of credit
The best alternative to a promissory note will depend on the specific needs of the issuer and payee.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of a promissory note?
A promissory note is a written promise to pay a specified sum of money to a designated payee on a specific date or on demand.
What are the key elements of a valid promissory note?
A valid promissory note must include the following elements: the amount of the loan, the interest rate (if any), the maturity date, the signatures of both the borrower and the lender, and a statement that the note is a legally binding obligation.
What are the potential consequences of defaulting on a promissory note?
Defaulting on a promissory note can result in legal action, damage to creditworthiness, and additional fees and penalties.